近日,國際人工智能領域頂級學術會議AAAI 2026(Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence)公佈了論文錄用結果,澳門科技大學創新工程學院-計算機科學與工程學院7篇學術論文成功獲得接收。AAAI 2026主會議共收到23,680份有效投稿,最終錄用4,167篇論文,僅17.6%整體錄用率。
AAAI會議由國際人工智能促進協會主辦,自1979年創立以來,在全球人工智能研究領域具有極高聲譽,也是中國計算機學會(CCF)推薦的A類國際頂級學術會議。澳科大此次入選的7篇論文,聚焦於三維動態場景重建、擴散模型的高效採樣、三維點雲理解、基於知識蒸餾的三維物體檢測、圖像內容理解與描述、AI模型脆弱性研究以及用於推薦系統的圖神經網絡等人工智能前沿關鍵領域,不僅具有重要的理論創新價值,同時展現出廣闊的應用前景。
近年來,澳科大系統構建了人工智能學士課程及博士課程的較完整人才培養體系,並配套設立了人工智能及機器學習實驗室等多個專業科研平台,匯聚了包括講座教授、特聘教授、教授等在內的一支高水平教學科研團隊。學科建設的持續深耕已獲國際多個主流排名認可:在最新發佈的U.S. News 2025/2026全球大學學科排名中,澳科大人工智能學科排名全球第88位;在上海軟科發佈的2025世界一流學科排名中,澳科大人工智能學科位列全球151-200區間。
澳科大創新工程學院-計算機科學與工程學院院長蔡占川表示,此次多篇高水平論文成功入選AI頂級會議,是學院長期堅持「科研與教學深度融合、理論與實踐並重」培養理念的生動體現與重要成果。未來,學校將繼續深化在人工智能領域的學科佈局,拓展高水平國際合作,依托現有的先進科研平台,為學生提供更前沿、更系統的學術訓練與科研實踐機會。
AAAI 2026接收的7篇論文簡介如下:
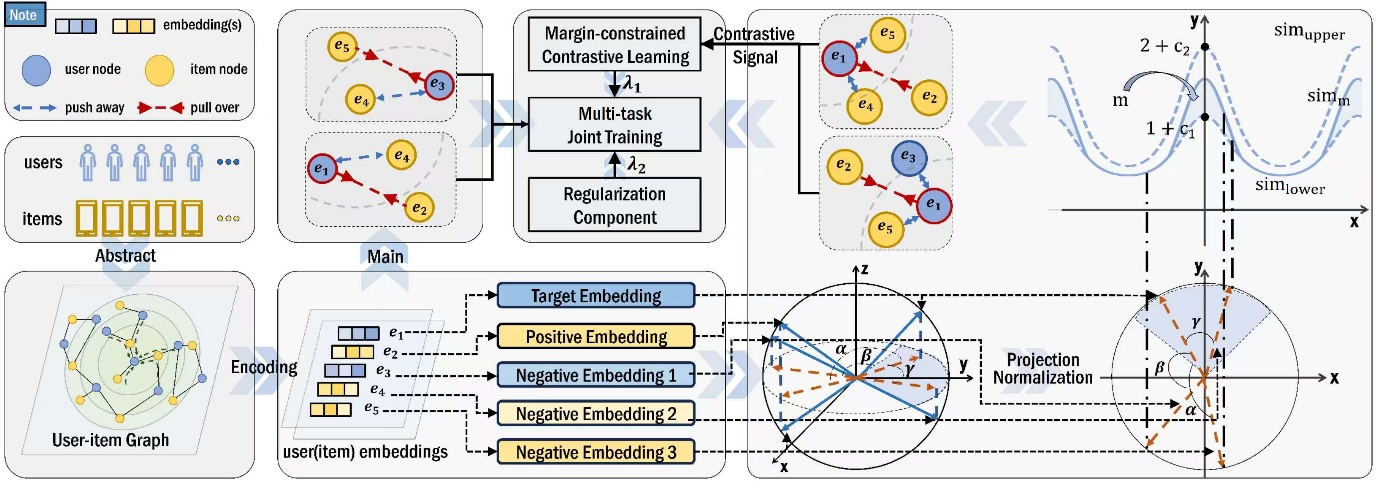
論文題目:MCGS: Markov Chain Gaussian Splatting for Dynamic Scenes Reconstruction
第一單位:Faculty of Innovation Engineering, Macau University of Science and Technology
作者信息:王煜中 博士研究生(第一作者),王文敏 教授(導師,通訊作者)

論文摘要:We present MCGS (Markov Chain Gaussian Splatting), a novel approach for high-fidelity dynamic scene reconstruction via combining Markov chain and 3D Gaussian splatting. Our method addresses the critical challenge of artifact-free temporal consistency in dynamic neural rendering. By integrating a Markov chain-based deformation network with multi-head temporal attention, MCGS effectively captures motion patterns and temporal dependencies, producing more accurate and stable 3D representations over time. The key innovations include: (1) a Markov Deform Network that models state transitions while preserving temporal coherence, (2) a temporal attention mechanism that adaptively weights historical states within a sliding window, and (3) strategic noise injection during training to enhance model robustness and generalization. Experiments on representative dynamic scene datasets demonstrate that MCGS outperforms previous methods in both visual quality and temporal coherence, while maintaining competitive rendering speed and efficiency. These results suggest the practical applicability of our approach to real-world dynamic scene understanding and synthesis.
論文題目:Hierarchical Schedule Optimization for Fast and Robust Diffusion Model Sampling
第一單位:Faculty of Innovation Engineering, Macau University of Science and Technology
作者信息: 朱愛華 博士研究生(第一作者),趙慶林 教授(導師,通信作者)

論文摘要:Diffusion probabilistic models have set a new standard for generative fidelity but are hindered by a slow iterative sampling process. A powerful training-free strategy to accelerate this process is Schedule Optimization, which aims to find an optimal distribution of timesteps for a fixed and small Number of Function Evaluations (NFE) to maximize sample quality. To this end, a successful schedule optimization method must adhere to four core principles: effectiveness, adaptivity,
practical robustness, and computational efficiency. However, existing paradigms struggle to satisfy these principles simultaneously, motivating the need for a more advanced solution. To overcome these limitations, we propose the HierarchicalSchedule-Optimizer (HSO), a novel and efficient bi-level optimization framework. HSO reframes the search for a globally optimal schedule into a more tractable problem by iteratively alternating between two synergistic levels: an upperlevel global search for an optimal initialization strategy and a lower-level local optimization for schedule refinement. This process is guided by two key innovations: the Midpoint Error Proxy (MEP), a solver-agnostic and numerically stable objective for effective local optimization, and the SpacingPenalized Fitness (SPF) function, which ensures practical robustness by penalizing pathologically close timesteps. Extensive experiments show that HSO sets a new state-of-the-art for training-free sampling in the extremely low-NFE regime. For instance, with an NFE of just 5, HSO achieves a remarkable FID of 11.94 on LAION-Aesthetics with Stable Diffusion v2.1. Crucially, this level of performance is attained not through costly retraining, but with a one-time optimization cost of less than 8 seconds, presenting a highly practical and efficient paradigm for diffusion model acceleration.
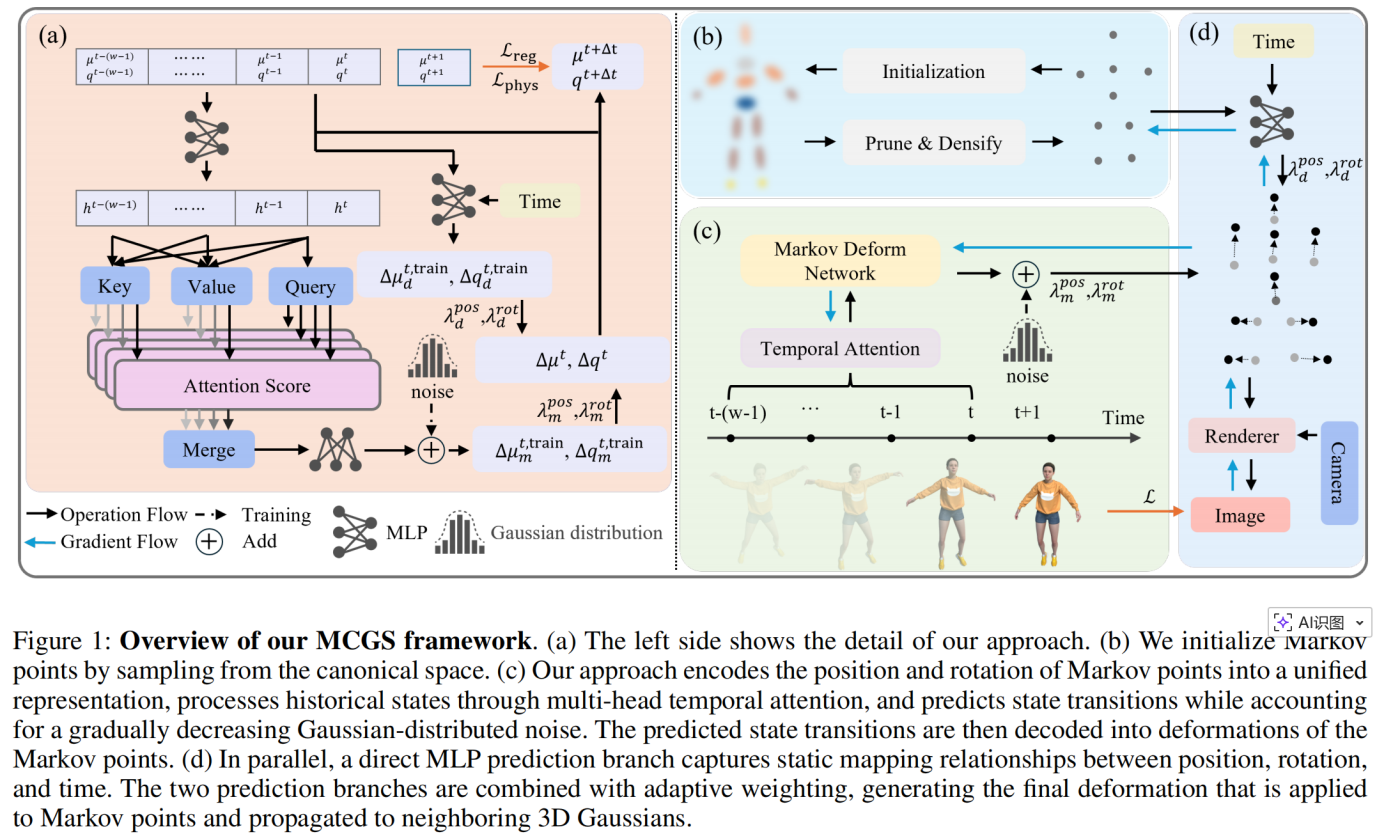
論文題目:Distilling Future Temporal Knowledge with Masked Feature Reconstruction for 3D Object Detection
第一單位:Faculty of Innovation Engineering, Macau University of Science and Technology
作者信息:鄭皓文 博士研究生(第一作者),梁延研 副教授(導師,通訊作者)

論文摘要:Camera-based temporal 3D object detection has shown impressive results in autonomous driving, with offline models improving accuracy by using future frames. Knowledge distillation (KD) can be an appealing framework for transferring rich information from offline models to online models. However, existing KD methods overlook future frames, as they mainly focus on spatial feature distillation under strict frame alignment or on temporal relational distillation, thereby making it challenging for online models to effectively learn future knowledge. To this end, we propose a sparse query-based approach, Future Temporal Knowledge Distillation (FTKD), which effectively transfers future frame knowledge from an offline teacher model to an online student model. Specifically we present a future-aware feature reconstruction strategy to encourage the student model to capture future features without strict frame alignment. In addition, we further introduce future-guided logit distillation to leverage the teacher’s stable foreground and background context. FTKD is applied to two high-performing 3D object detection baselines, achieving up to 1.3 mAP and 1.3 NDS gains on the nuScenes dataset, as well as the most accurate velocity estimation, without increasing inference cost.
論文題目:PointMC: Multi-view Consistent Encoding and Center-Global Feature Fusion for Point Clouds Understanding
第一單位:Faculty of Innovation Engineering, Macau University of Science and Technology
第一作者:俞新星 博士研究生(第一作者),劉阿建 澳門青年學者計劃博士後(通訊作者),梁延研 副教授(導師, 通訊作者)

論文摘要:Point cloud tasks have recently benefited from Mamba-based architecture, which leverage state space modeling to achieve strong performance. Previous studies have primarily focused on network design while overlooking the importance of position encoding and relying on coarse-grained geometric feature aggregation. The former leads to semantic ambiguity due to inconsistent spatial relationships, while the latter results in geometric feature dispersion by overlooking finegrained local geometric details. To tackle the above problem, we propose a novel framework, PointMC, including Multiview Consistent Learnable Position Encoding (MCLPE) and Center-Global Feature Fusion (CGFF), to provide semantically coherent positional guidance for inter-patch and enable fine-grained geometric structure aggregation within intrapatch regions. Specifically, the proposed MCLPE module is inspired by a spatial structure modeling mechanism guided by physical constraints, leverages multi-view virtual reconstruction and a learnable strategy to dynamically constrain spatial relationships along patch boundaries, thereby enhancing the semantic consistency and representational clarity across inter-patch regions. Furthermore, considering the lack of local structural information within each patch, the CGFF module employs a dual-guidance mechanism based on center and global structures to effectively promote the aggregation of local geometric features. Extensive experiments on multiple benchmark datasets validate the effectiveness of PointMC, consistently outperforming existing state-of-the-art methods, and demonstrating superior capability in capturing both interpatch semantic consistency and intra-patch geometric details.

論文題目:OAD-Promoter: Enhancing Zero-shot VQA using Large Language Models with Object Attribute Description
第一單位:Faculty of Innovation Engineering, Macau University of Science and Technology
作者信息:許全星 博士生(第一作者),周玲 助理教授(導師,通信作者),黃如兵 副教授(導師)

論文摘要:Large Language Models (LLMs) have become a crucial tool in Visual Question Answering (VQA) for handling knowledge-intensive questions in few-shot or zero-shot scenarios. However, their reliance on massive training datasets often causes them to inherit language biases during the acquisition of knowledge. This limitation imposes two key constraints on existing methods: (1) LLM predictions become less reliable due to bias exploitation, and (2) despite strong knowledge reasoning capabilities, LLMs still struggle with out-of-distribution (OOD) generalization. To address these issues, we propose Object Attribute Description Promoter (OAD-Promoter), a novel approach for enhancing LLM-based VQA by mitigating language bias and improving domain-shift robustness. OAD-Promoter comprises three components: the Object-concentrated Example Generation (OEG) module, the Memory Knowledge Assistance (MKA) module, and the OAD Prompt. The OEG module generates global captions and object-concentrated samples, jointly enhancing visual information input to the LLM and mitigating bias through complementary global and regional visual cues. The MKA module assists the LLM in handling OOD samples by retrieving relevant knowledge from stored examples to support questions from unseen domains. Finally, the OAD Prompt integrates the outputs of the preceding modules to optimize LLM inference. Experiments demonstrate that OAD-Promoter significantly improves the performance of LLM-based VQA methods in few-shot or zero-shot settings, achieving new state-of-the-art results.
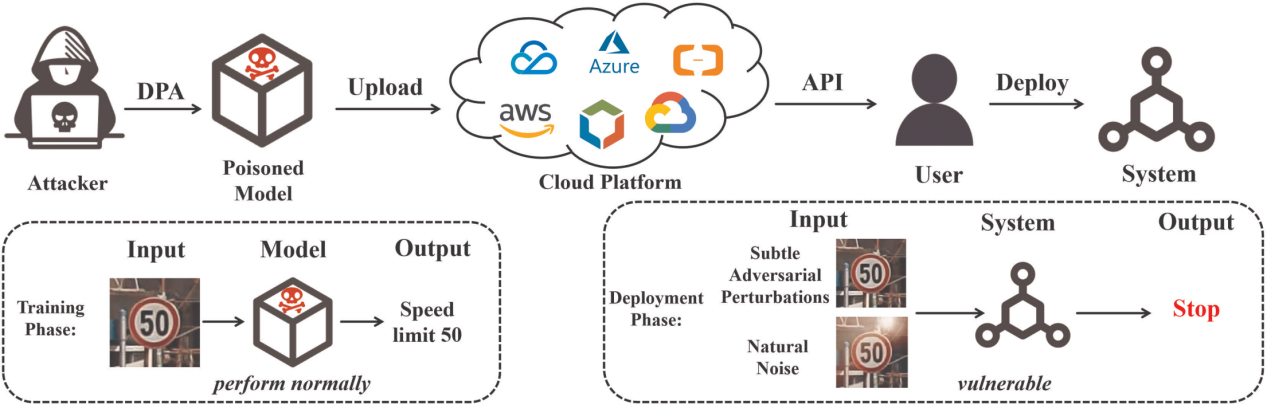
論文題目:Deferred Poisoning: Making the Model More Vulnerable via Hessian Singularization
第一單位:Faculty of Innovation Engineering, Macau University of Science and Technology
作者信息:何宇浩 博士生(第一作者),田晉宇 助理教授(導師,通信作者)

論文摘要:Recent studies have shown that deep learning models are very vulnerable to poisoning attacks. Many defense methods have been proposed to address this issue. However, traditional poisoning attacks are not as threatening as commonly believed. This is because they often cause differences in how the model performs on the training set compared to the validation set. Such inconsistency can alert defenders that their data has been poisoned, allowing them to take the necessary defensive actions. In this paper, we introduce a more threatening type of poisoning attack called the Deferred Poisoning Attack. This new attack allows the model to function normally during the training and validation phases but makes it very sensitive to evasion attacks or even natural noise. We achieve this by ensuring the poisoned model’s loss function has a similar value as a normally trained model at each input sample but with a large local curvature. A similar model loss ensures that there is no obvious inconsistency between the training and validation accuracy, demonstrating high stealthiness. On the other hand, the large curvature implies that a small perturbation may cause a significant increase in model loss, leading to substantial performance degradation, which reflects a worse robustness. We fulfill this purpose by making the model have singular Hessian information at the optimal point via our proposed Singularization Regularization term. We have conducted both theoretical and empirical analyses of the proposed method and validated its effectiveness through experiments on image classification tasks. Furthermore, we have confirmed the hazards of this form of poisoning attack under more general scenarios using natural noise, offering a new perspective for research in the field of security.
論文題目:Revisiting Contrastive Learning in Collaborative Filtering via Parallel Graph Filters
第一單位:Faculty of Innovation Engineering, Macau University of Science and Technology
作者信息:開放 碩士研究生(第一作者)

論文摘要:Graph Contrastive Learning (GCL) has recently emerged as a powerful paradigm for modeling user–item interactions and for learning high-quality representations in recommender systems. While existing GCL-based methods benefit from data augmentation and sampling strategies, they often overlook the inherent limitations of the contrastive objectives: 1) Stacking multiple Graph Convolutional Network layers to capture high-order information often causes the oversmoothing phenomenon, where node representations become overly similar. 2) Structurally similar negative sample pairs may exhibit high cosine similarity, causing gradient saturation during representation optimization. To address the above challenges, we revisit matrix factorization in recommendation models and uncover its implicit connection to a parallel graph filter bank. This perspective reveals how overly aggressive low-pass or high-pass filtering distorts feature distributions, contributing to gradient saturation. Building on this insight, we propose Light Cosine Similarity Collaborative Filtering (LightCSCF), a margin-constrained method that improves gradient optimization in contrastive learning by focusing on structurally hard examples, alleviating both gradient saturation and boundary over-smoothing. Extensive experiments on three real-world datasets demonstrate that LightCSCF consistently outperforms state-of-the-art baselines in recommendation accuracy and robustness to data sparsity.