Acne is a prevalent skin condition caused by the blockage of subcutaneous hair follicles, often triggered by hormonal fluctuations, oily cosmetics, certain medications, excessive sweating, and skin friction. The accumulation of sebum and dead skin cells can clog pores, leading to rapid bacterial growth inside. To address this issue, a joint research team led by Professor Tang Jianxin and Dr. Liu Yiming from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at Macau University of Science and Technology has recently made significant progress in the field of wearable smart devices. The team developed a stretchable self-powered drug delivery system using clindamycin as an antibacterial agent, powered by a biocompatible high-performance magnesium-oxygen (Mg-O₂) battery.
Based on the principle of iontophoresis, the direct current generated by the integrated battery acts on a self-developed clindamycin-loaded drug layer, enabling the synergistic and directional transport of clindamycin and electrolyte ions to precisely target acne-affected areas. By adjusting the battery power output, the drug delivery rate can be precisely controlled. Benefitting from advanced mechanical design and material selection, the entire system is fully stretchable and biocompatible, achieving up to 100% stretchability within the yield limit. This allows the system to conform effectively to most areas of the human body for acne treatment (Figure 1). The efficacy of this self-powered drug delivery system was further validated through in vitro and in vivo biological experiments, demonstrating a groundbreaking paradigm for acne treatment—prolonging antibiotic efficacy cycles while ensuring long-term wearing comfort. This research work has been published in the renowned journal ACS Nano, titled "Self-Driven, Stretchable Drug Delivery Electronics for Acne Treatment." Dr. Liu Yiming is the first and corresponding author of the paper, and MUST is the first affiliated institution.
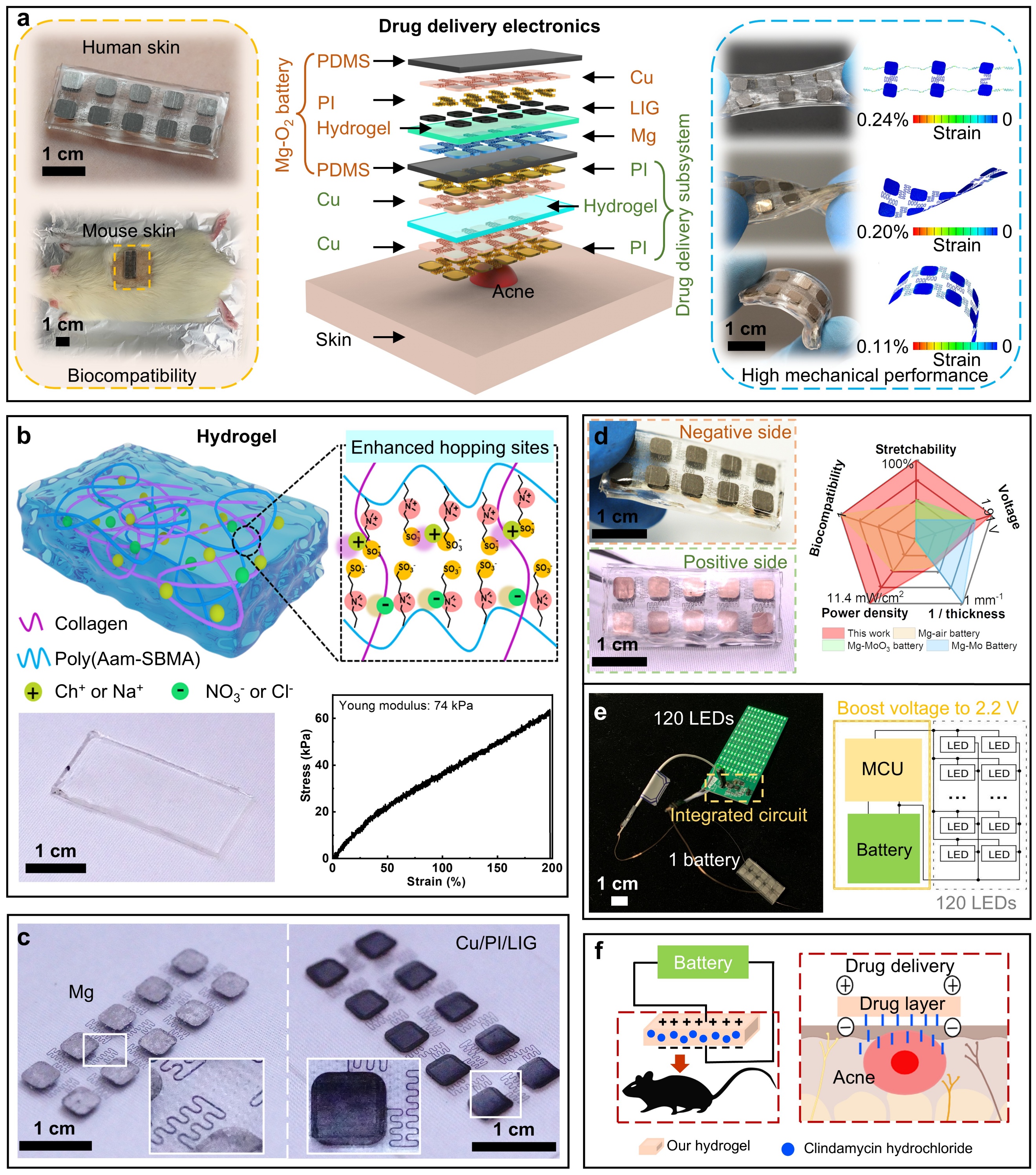
Figure 1. Architecture of the SSDDE system.
Paper Link: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsnano.5c09857




























